A proximity sensor is a device that senses another object when it is close to it. Most proximity sensors only indicate the presence of an object within their sensing area. Proximity sensors detect the presence of objects without physical contact. There are a variety of proximity sensors to suit all types of applications. Typical applications include inspection, positioning, inspection, and counting of automated machines and manufacturing systems. In this article, we’ll discuss proximity sensors in detail, such as what a proximity sensor is, what it does, and how a proximity sensor works.
Table of Contents
What Are Proximity Sensors?
A proximity sensor is a component designed to detect the presence of an object without physical contact. They are non-contact devices ideal for handling delicate or unstable objects that can be damaged by contact with other types of sensors.
This contactless operation also means extended life for most types of proximity sensors (excluding types such as magnetic proximity sensors). This is because they have semiconductor outputs, which means there are no contacts for the output.
Read More: What Are Parking Sensors?
Types of Proximity Sensor
There are three main types of proximity sensors – capacitive, ultrasonic, and inductive. Each has specific characteristics and is best suited to different applications. You can read more about each type in the sections below:
Capacitive Proximity Sensors

Capacitive proximity sensors have a pair of parallel plates, similar to standard capacitors. They work when the object produces a change in capacitance that triggers the sensor. Capacitive sensors are designed for use with non-ferrous materials and are ideal for close-range applications such as liquid level detection and monitoring.
It should also be noted that capacitive sensors may be affected by their environment and possible interactions with other sensors. This can include anything from ambient temperature to other nearby objects. Therefore, precautions should be taken when installing these sensors to avoid interference from other objects or sensors.
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors

Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves, which are reflected or absorbed by anything within the sensing range. They are versatile and can be used with a wide variety of materials and object types. Ultrasonic sensors are also relatively high-speed, so they can be used for detection over longer distances than other types. They are also suitable for detecting objects with different surface properties. Only a few example applications include continuous level control and industrial automation systems.
Inductive Proximity Sensors

Inductive proximity sensors have a wound iron core. When an object enters the sensing range, the inductance of the coil changes, which activates the sensor. These parts are used with ferrous materials, usually in close proximity, and some types may also be found in hazardous environments.
Similar to capacitive proximity sensors, inductive sensors are also affected by interactions with other sensors and environmental influences. Careful installation is required to ensure the sensor is effective and not adversely affected by surrounding sensors or metal objects.
Magnetic Proximity Sensors

Magnetic sensors are designed to measure the presence or absence of an object. They achieve this by using an external magnetic field, and as the name suggests, they only work with ferromagnetic objects. These components are typically high-speed, making them suitable for measuring fast rotational velocity, for example.
Proximity Sensor Circuit-Target Size
A standard target is a target made of mild steel with a flat and smooth surface and a thickness of 1mm. There are many grades of steel, mild steel is composed of carbon and iron (in higher content).
The side of a standard target with a muting sensor will be equal to the diameter of the sensing face. The target side with an unshielded sensor is equal to the larger of the two, which is three times the diameter of the sensing face or the rated operating range.
Features of the Proximity Sensor
To understand what a proximity sensor is all about, we’re going to understand what it does. Its characteristics are as follows:
- 1. Non-contact sensing
Proximity sensors detect objects without touching them, so there is no wear or damage to them. Devices such as limit switches detect objects by touching them, but proximity sensors are able to detect the presence of objects electronically without any touch.
- 2. Not affected by surface conditions
Proximity sensors detect physical changes in objects, so they are almost completely unaffected by the color of the object’s surface.
- 3. Wide range of application
Unlike traditional optical detection, proximity sensors are suitable for wet conditions and a wide temperature range. They can be used in the following temperature range −40 to 200°C.
Proximity sensors are also available in mobile phones like Android or IOS devices. It consists of simple infrared technology that turns the display on/off depending on your usage. For example, when a phone is on a call, it turns off your screen so you don’t accidentally activate it when you hold it near your cheek!
- 4. Longer service life
Since the proximity sensor uses semiconductor outputs, there are no moving parts that depend on the duty cycle. As a result, it tends to last longer than conventional sensors!
- 5. High-speed response
Proximity sensors offer a higher speed response rate than switches that require contact for sensing.Unlike optical detection methods, proximity sensors are suitable for use where water or oil is used. Detection is hardly affected by dirt, oil, or water on the detected object. Models with fluororesin housing also have excellent chemical resistanceUnlike switches that rely on physical contact, proximity sensors are affected by ambient temperature, surrounding objects, and other sensors. Both inductive and capacitive proximity sensors are affected by interactions with other sensors. Therefore, care must be taken during installation to prevent mutual interference. (See all Proximity Sensor Safety Precautions for proper use.) Care must also be taken to prevent the influence of surrounding metal objects on the inductive proximity sensor, and to prevent the influence of all surrounding objects on the capacitive proximity sensor.
How Do Proximity Sensors Work?
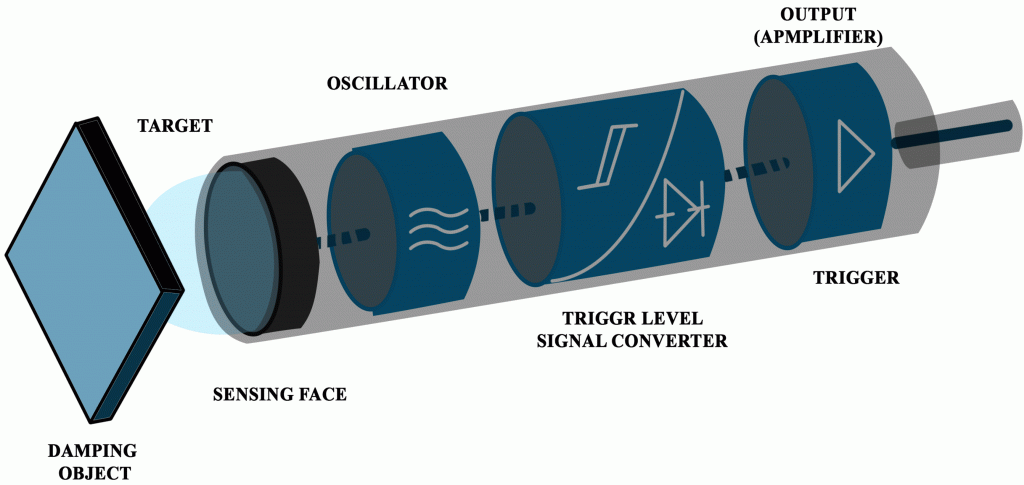
At its simplest, proximity sensors work by transmitting data about the presence or movement of an object into an electrical signal. When objects come into their range, they output an on the signal. There are some key differences in how different proximity sensors work, as described below:
- How Capacitive Proximity Sensors Work
Capacitive proximity sensors work by detecting changes in capacitance between the sensor and an object. Factors such as distance and object size can affect capacitance. The sensor only detects the volume change that occurs between the two.
- How Inductive Proximity Sensors Work
Inductive sensors work by detecting eddy currents that result in magnetic losses caused by external magnetic fields on conductive surfaces. The detection coil generates an alternating magnetic field and detects impedance changes through the generated eddy currents.
Proximity Sensor Applications
Proximity sensors can be used in a range of environments and in many different applications. They are beneficial for any application that needs to detect objects within a defined range. This may include:
- Standard object position detection
- Transportation, Logistics and Supply Chain
- Inspection and Quality Assurance
- Process control
- Liquid level detection
- food processing and manufacturing
- agriculture
They can also be used in environments where oil or water are used, offering solid advantages over other detection methods. Capacitive proximity sensors can detect media such as water, resin, and metal based on the dielectric constant of the object. Different types of sensors are best for detecting different objects, as described below:
- Capacitive Proximity Sensors – Metal, Liquid, Water, Resin, Powder
- Inductive proximity sensors – metals, including aluminum, copper, brass, and iron
- Magnetic Proximity Sensors – Magnets
Proximity sensors are also suitable for environments where temperature fluctuations or extreme temperatures are common. Although temperature compatibility depends on the specific model, as a general rule, proximity sensors can be used in the temperature range of -50°C to 100°C.
Summary
Proximity sensors are common in smartphones these days. It uses infrared radiation invisible to the normal human eye.
Infrared light emitting diodes emit infrared radiation, and the radiation will rebound from any nearby surface. The reflected light is detected by an infrared receiver next to the transmitter. Depending on the distance between the obstacles and the sensor, the light intensity falling on the receiver will change.
Therefore, high-intensity light reflected back means there is an obstacle or surface nearby. These sensors are usually digital (and sometimes analog).
I hope this article can help you understand the working principles, basic knowledge, and functions close to the sensor.



